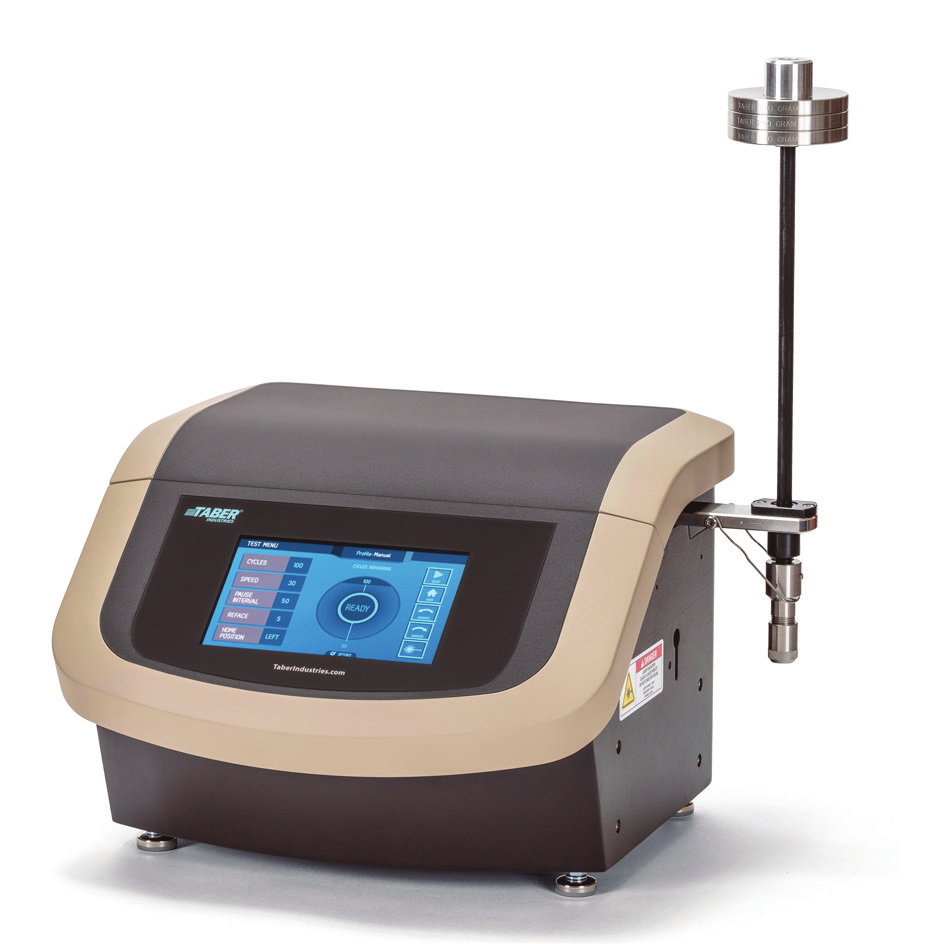
The Linear Abraser uses a floating head to follow the contours of the specimen which permits the testing of finished products.
The limitations of specimen size and shape are virtually nonexistent, making the Linear Abraser ideal for testing molded plastic parts, automotive components, painted and coated parts, or optical products.
The Wearaser™ abrasive, similar in configuration to a standard pencil eraser, employs the same high quality materials found in other Taber® Abrasive Media, assuring consistent test results.
The Model 5770 features adjustable stroke length, speed, load, and a wide variety of Taber® Wearaser™ abrading media, allowing the customization of test parameters to suit virtually any requirement.
The Linear Abraser can be configured with optional test attachments to evaluate the relative resistance of a material’s surface to damage such as wear and abrasion, scratch, gouge, scrape, rub, crocking, and more.
Please submit a Request for Quotation (RFQ) for the Taber Linear Abraser and any accessory or replacement items. Refer below to a description of the standard and optional components.
NOTE: This video showcases an older Abraser model, but the test procedures are largely identical.
The PDF below contains the Taber® Linear Abraser Model 5770 Set-Up chart. It is provided to assist in establishing specific test loads for the Model 5770:
Taber® Linear Abraser Model 5770 Set-Up Chart
Complete Data Sheets for Taber® Abraser Model 5770:
Ask for Price

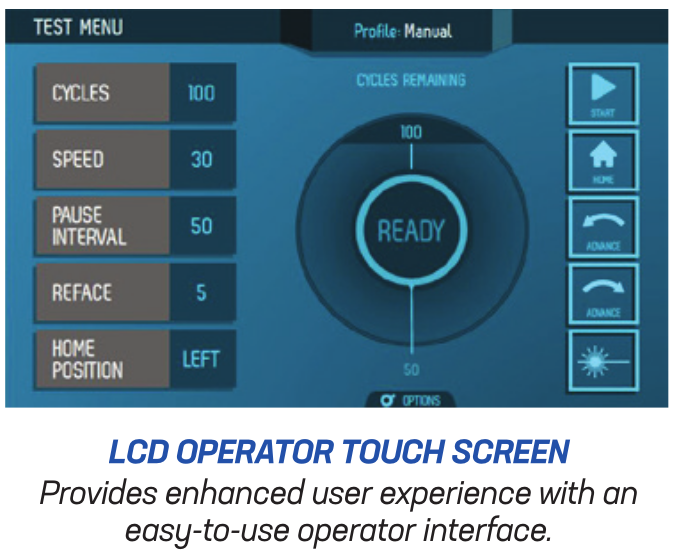
- LCD touch screen interface
- 11 standard stroke lengths (from 0.2 to 4.0 in.)
- Variable stroke speed (from 2 to 75 cycles per minute)
- Variable load (from 350 to 2400 gram) using optional auxiliary weight disks
- Laser alignment guide
- Screen displays test cycles or strokes
- The safety switch will stop a test when the lid is raised
- 115 / 230 VAC Switchable Power Supply
- CE Marked.
| Description | Quantity |
| Wearaser Collet Kit, Stainless Steel | 1 |
| 250g Auxiliary weight disc | 3 |
| CS—10 Wearaser Abrasive Media | 10 |
| H-18 Wearaser Abrasive Media | 1 |
| Electrical Cord | 1 |
| S-14 Refacing Strips | 1 |
| S-12 Hand Brush | 1 |
Spherical Tips (threaded)
Because of its symmetrical characteristics, spherical tips allow for the stylus to contact the test surface without concern about orientation or alignment. This feature makes spherical tips the most common shape utilized for scratch testing.
Conical – These scratch tips are made from tungsten carbide brazed onto a 0.375″ diameter stainless steel body. A #8-32UNC-2A threaded post allows this tip to be screwed directly to the bottom of the Linear Abraser spline shaft or Reciprocating Abraser weight post. All tips include a 60° angle.
- Conical Scratch Tip, 0.30mm Diameter
- Conical Scratch Tip, 0.60mm Diameter
- Conical Scratch Tip, 0.75mm Diameter
- Conical Scratch Tip, 1.00mm Diameter

Hemispherical – A tungsten carbide ball is brazed into a 0.375″ diameter stainless steel body. A #8-32UNC-2A threaded post allows this tip to be screwed directly to the bottom of the Linear Abraser spline shaft or Reciprocating Abraser weight post. The 1.0mm diameter tips include a 60° angle and the 7mm diameter tip includes a 75° angle.
Taber also offers a 1.0mm diameter tip that includes a steel ball (HRC 60-66). Similar to the tungsten carbide tip described above, the steel ball tip includes a 60° angle.
Diamond Tool Holders
Taber offers two industry accepted diamond tools. The diamond tip is conical and lapped to a 0.092″ diameter, 0.531″ long stainless steel rod. The 3 mil and 3.5 mil radius tools include a 90° angle, and the 0.3mm radius too includes a 60° angle.
-
3 mil radius point – Model 139-55
-
3.5 mil radius point – Model 139-56
- 0.3mm radius point – Model 139-52
Either tool requires one of the following attachments to hold the diamond tool securely.
The Diamond Tool Holder is a cylindrical holder that the diamond tool is inserted into and held in place by a set screw. A #8-32UNC-2A threaded post allows this tip to be screwed directly to the bottom of the Linear Abraser spline shaft or Reciprocating Abraser weight post.
The Scratch Kit includes both diamond tools along with a 7x measuring magnifier. This attachment is available as steel [98g] or aluminum [33g], and mounts to the bottom of the Linear Abraser spline shaft or Reciprocating Abraser weight post.
Multi-Mar Scratch Attachment
Designed to accommodate four different styli, the Multi-Mar Scratch Attachment is available in a 45° or 90° orientation. This attachment is typically used to evaluate plastics, paints, and coatings for resistance to scratch and mar.
Loop Stylus – Made from 1″ long by 1/16″ diameter tool steel heat treated to HRC 55-61 with an outside radius of 0.128″ and 8 RMS surface finish (included with each Multi-Mar Scratch Attachment).
Needle Stylus – Made from stainless steel with a 1.5 mm diameter tip, hardness of HRC 55-61 and 8 RMS surface finish.
Hoffman Type Stylus – Made from tool steel heat treated to HRC 55-61 with a 0.275″ diameter contact arc and 8 RMS surface finish.
Standardized Copper “Coin” – Manufactured from copper alloy 101, this coin has a 0.75″ diameter and is 0.06″ thick with an edge radius of R0.010″. The hardness of this tool was selected to simulate the hardness of the human fingernail, and is intended to provide a repeatable “Fingernail Scratch” or coin scrape test. It is also useful in determining the durability of scratch off applications used on lottery tickets and similar products.
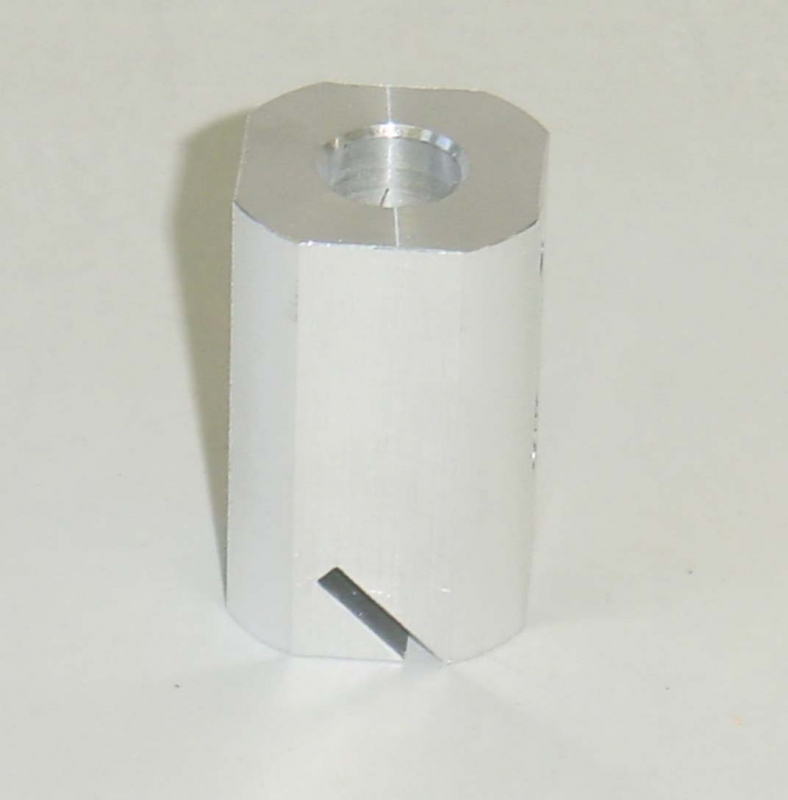

Coin Holder
The Coin Holder Attachment is available in three different angles, and includes a 0.078″ wide slot which is 0.45″ deep. The standardized copper coin may be used with this holder as well as other coins in circulation. [Note: Use caution when testing with a coin that has been in circulation, as wear may influence the condition of the edge.]
-
45°Angle Coin Holder
-
60°Angle Coin Holder
-
75°Angle Coin Holder
Pencil Hardness
The Pencil Hardness Kit provides a rapid, economical and reliable means of evaluating film hardness of paints and coatings in accordance with ASTM D3363 and ISO 15184. A holder orients the pencil at a 45° angle, and the test involves pushing it a distance of 1/4 inch. The test starts with the hardest pencil (6H) and continues with the next softer pencil until the operator identifies the pencil that will not cut into or gouge the film (pencil hardness), or the pencil that will not scratch the film (scratch hardness). Pencil core hardnesses are graded using the following scale from softest (6B) to hardest (6H):
6B – 5B – 4B – 3B – 2B – B – HB – F – H – 2H – 3H – 4H – 5H – 6H
Although the HB grade is considered to be the standard, there may be variation from one manufacturer to another. Also, it has been observed that German HB’s tend to be harder than United States HB’s, which are slightly more hard than Japanese HB’s.

Mar Attachments
The Scotch Brite® Kit can be used to evaluate material resistance to abrasion and damage caused by “scrubbing”. An aluminum block that is 1.18″ square provides a flat surface to which ScotchBrite® General Purpose Pads or ScotchBrite® Light Duty Pads can be attached.
Taber’s Square Finger Holder is designed with either a 10mm or 20mm square contact area and is ideal to use with steel wool when testing the mar resistance of material surfaces. The holder includes a compressible rubber pad which has been affixed to the contact surface, and is intended to keep the steel wool in place during testing.
| Reference | Title | Scope |
| AATCC Test Method 8 | Colorfastness for Crocking | This test method is designed to determine the amount of color transferred from the surface of colored textile materials to other surfaces by rubbing. It is applicable to textiles made from all fibers in the form of yarn or fabric whether dyed, printed or otherwise colored. |
| AATCC Test Method 165 | Colorfastness for Crocking | This test method is designed to determine the amount of color transferred from the surface of colored textile materials to other surfaces by rubbing. It is applicable to textiles made from all fibers in the form of yarn or fabric whether dyed, printed or otherwise colored. |
| ASTM A975 | Standard Specification for Double-Twisted Hexagonal Mesh Gabions and Revet Mattresses (Metallic-Coated Steel Wire or Metallic-Coated Steel Wire With Poly(Vinyl Choride) (PVC) Coating) {Section 13.1.5 - Abrasion Resistance Test} | This specification covers gabions and revet mattresses produced from double-twisted metallic-coated wire for lacing wire, stiffeners, and fasteners used for manufacturing, assembling, and installation of the product. This specification also covers gabions and revet mattresses in which the wire mesh, lacing wire, and stiffeners are poly(vinyl choride) (PVC) coated after the metallic coating. |
| ASTM D6279 | Standard Test Method for Rub Abrasion Mar Resistance of High Gloss Coatings | This test method covers procedures for evaluating the relative mar resistance of a series of high gloss coatings applied to a flat, rigid surface. Wet rub and dry rub abrasion tests are described. To fully characterize a coating’s mar resistance, both tests should be run. |
| ASTM F3300 | Standard Test Method for Abrasion resistance of Flexible Packaging Films Using a Reciprocating Weighted Stylus | This test method covers the determination of the abrasion resistance of flexible non-conductive films and packaging materials using a weighted stylus that wears completely through a film by oscillating or reciprocating back and forth along a linear path until an electrical circuit is completed shutting down the test. |
| ASTM D3363 | Standard Test Method for Film Hardness by Pencil Test | This test method covers a procedure for rapid, inexpensive determination of the film hardness of an organic coating on a substrate in terms of drawing leads or pencil leads of known hardness. |
| CFFA-7 STM2013 | Standard Test Methods Chemical Coated Fabrics and Film Section 7 | Section I covers test procedures for coated fabrics; Section II covers test procedures for films. These tests include adhesion of coating, weight, resistance to cold, blocking, aging, abrasion resistance, hydrolytic stability, volatility, tensile, tearing strength, and many more. |
| ECCA-T11 | M.E.K. Solvent Rubbing Test | This test method defines the procedure of evaluating the degree of curing by determining the resistance of an organic coating on a metallic substrate to M.E.K. or other solvents. |
| EN 3475-503 | Aerospace series - Cables, electrical, aircraft use - Test methods - Part 503: Scrape abrasion | This standard specifies a method of measuring the resistance to abrasion by scraping. It shall be used together with EN 3475-100. |
| EN 6059-403 | Aerospace Series - Electrical cables, installation, protection sleeves. Test Methods Part 403: Scrape abrasion | This standard specifies a method of measuring the scrape abrasion of protection sleeve for electrical cable and cable bundles. It shall be used together with EN6059-100. |
| EN 13523-11 | Coil coated metals - Part 11: Resistance to solvents (rubbing test) | This part of EN 13523 specifies the procedure for evaluating the degree of curing by determining the resistance of an organic coating on a metallic substrate to solvents. |
| EN 16268 | Perfomance of reflecting surfaces for luminaires | Pertains to the optical performance of untreated or coated materials supplied in plane sheet or strip form for use as a plane or formed reflector as well as preformed reflectors both as originally produced and after prescribed tests to determine probable maintained performance in service. |
| Fed 191A - Method 5651 | Federal Standard for Textile Test Methods | This method is intended for determining the resistance of cloth to crocking. Crocking in this case refers to the transfer matter from one cloth to another cloth with which it may come in woven or knitted of coloring contact. This method is applicable to cloth of all fibers whether dyed, printed, impregnated, or otherwise colored. The method is particularly applicable to cloth of solid color, although variegated cloth may be tested if the colored area is of sufficient size. The method also includes provisions for testing the crocking of white or light functionally finished cloths against dark colored cloth when required by the cloth specification. Wet and dry crocking may be determined by this method. Unless otherwise specified in the procurement document, both wet and dry crocking are considered in rating the resistance to crocking as determined by this method. |
| Florida DOT FM 5-594 | Florida Method of Test for Wear Resistance of Surface Applied Detectable Warning Surfaces | This method covers the determination of wear resistance of Detectable Warning Surfaces (mat) by use of a linear abrading techique. This test method defines abrasive wear by determining volume loss for the domes of these materials. |
| Ford Laboratory Test Method BI 161-01 | Mar Resistance Determination for Automotive Coatings | This procedure is used to determine the mar resistance of automotive coatings. |
| Ford Laboratory Test Method BN 107-01 | Dynamic Sealing Performance Specification | This procedure is used to determine the amount of color transfer from the surface of visible interior trim materials to other surfaces by rubbing. |
| General Motors GM9150P | Resistance to Marring and Scuffing | OBSOLETE: This procedure is used to determine the ability of a surface to resist scuffing or marring. |
| General Motors GMW14130 | Resistance to Marring or Scuffing | The purpose of this procedure is to determine the ability of a surface to resist scuffing or marring. Scuffing is defined as permanent damage to the coating. An example of scuffing would be a break in the topcoat with visible flakes of coating caused by scraping by the paperclip. Marring is defined as no break or penetration of the coating, only visible trenching or marking detectable. The marring may or may not be permanent. An example of marring would be a furrow created by the paperclip that does not break or permanently disturb the coating. |
| General Motors GMW14327 | Abrasion Protection Textile Sleeves | This specification covers material and performance requirements for expandable braided monofilament flexible sleeving, heat shrinkable woven sleeving and self-closing sleeving for abrasion resistant and anti-rattle applications. Typical applications include; wiring bundling in passenger compartment and underhood applications, protection of hoses, insulated wires, rods and tubing. {Table 3 only} |
| General Motors GMW14664 | Powder Coat Finish | This specification details the minimum performance, campatibility, and processing requirements for initial material approval of powder topcoats. |
| General Motors GMW16740 | Tape for Wiring Harness | This standard specifies dimensions, test methods and requirements for harness tapes. This standard is shall be used for all passenger cars and light duty truck wire harnesses to evaluate and classify wire harness tapes for a given application. Class designations are defined in Table 1 for the various temperature ranges encountered in/on vehicles. {Section 4.9 - Abrasion Resistance} |
| ISO 105-x12 | Textiles tests for colour Fastness - Part x12 colour fastness to rubbing | Specifies a method for determining the resistance of the colour of textiles of all kinds, including textile floor coverings and other pile fabrics, to rubbing off and staining other materials. The method is applicable to textiles made from all kinds of fibres in the form of yarn or fabric, including textile floor coverings, whether dyed or printed. Two tests may be made, one with a dry rubbing cloth and one with a wet rubbing cloth. |
| ISO 6722 | Road Vehicles 60V and 600V single core cables - Dimensions, test methods and requirements | This International Standard specifies the dimensions, test methods, and requirements for single-core 60 V cables intended for use in road vehicle applications where the nominal system voltage is ≤ (60 V d.c. or 25 V a.c.). It also specifies additional test methods and/or requirements for 600 V cables intended for use in road vehicle applications where the nominal system voltage is greater than > (60 V d.c. or 25 V a.c.) to ≤ (600 V d.c. or 600 V a.c.). It also applies to individual cores in multi-core cables. |
| ISO 8980-5 | Ophthalmic optics - Uncut finished spectacle lenses | Specifies the requirement and test method for spectacle lens surfaces that are claimed to provide a basic level of abrasion resistance including those with coatings. A lens claimed to be abrasion-resistant shall meet the requirements on both front and back surfaces.Lens powers and surface form is restricted for testing, however test results are applicable to claims for lenses and lens surfaces with identical properties other than the lens power or surface radius. |
| ISO 15184 | Paints and Varnishes - Determination of Film Hardness by Pencil Test | This international standard is one of a series of standards dealing with the sampling and testing of paints, varnishes, and related products. It specifies a method for determining the film hardness by pushing pencils of known hardness over the film. The test can be performed on a single coating of paint, varnish, or related product, or on the upper layer of a multicoat system. |
| JASO D611 | Automotive parts - Unscreened low-voltage wire | This standard specifies low-voltage cables (hereinafter referred to as "cables") used as unscreened single-core low-voltage cables for automobiles, excluding AV (low-voltage cables for automobiles) specifies JIS C3400. In addition, this standard also applies to individual cores comprising a multi-core cable. The rated voltages for this cable shall be 25 VAC and 60 VDC. {5.7.2 Scrape Abrasion test} |
| JIS L 0849 | Test Methods for Colorfastness to Rubbing | This standard specifies the methods for determining the resistance of the colour of dyed textiles to rubbing. |
| Joint Industry Fabric Standards and Guidelines | Colorfastness to Crocking | This test method is intended for pile fabrics constructed by weaving or knitting techniques. This test method is not intended for flocked or chenille fabrics. |
| MIL-C-675C | Military Specification Coating of Glass Optical Elements (Anti-Reflection) | This specification establishes the minimum optical and durability requirements for magnesium fluoride interference films used as anti-reflection coatings on optical materials. |
| SAE J 861 | Method of Testing Resistance to Crocking of Organic Trim Materials | This test can be used to determine the resistance to crocking (color rub-off) of organic trim materials such as fabrics, vinyl coated fabrics, leather, coated fiberboard and carpet. |
NOTE: Optional accessories may be required to comply with these test standards.
ASTM, D2197, adhesion, balanced beam, scrape adhesion, tester, scrape, 25.220.60, scrape abrasion, D5178, mar resistance, balanced beam scrape adhesion, mar tester, balanced beam tester, coatings, mar, organic mar resistance, D6279, aluminum, coatings, gloss, wet rub, dry rub, D6037, grit, powder, rub test, scratch, 25.220.99, F1319, copying, crockmeter, crock meter, crocking, impact printers, inked ribbons, MICR, non-impact printers, OCR, smudge resistance, thermal transfer ribbons, toner images, AATCC Method 8, AATCC, Method 8, ISO 105-X12, ISO, 105-X12, 59.080.01, colour fastness to rubbing, colour fastness, colourfast, rubbing, rub test, color fast, colorfast, colorfastness, 6722, ISO 6722, road vehicles, voltage, cable, single core, multi-core, 43.040.10, Taber Abrasion Tester, Taber abraser, abraser, Taber, abrasion, abrasion tester, abrasion test, abrasion resistance, linear abrader.